- 최대한 범용성 있는 메서드를 만들어야 함
- 매서드 이름만 맞는 코드만 넣어야 나중에 혼란이 없다.
import java.util.Scanner;
//사칙연산 계산기 try-catch를 사용자매서드로 만들기! ver.2
public class Quiz_08 {
public static int inputnumber(String msg, String er){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int result =0;
while(true) {
try {
System.out.print(msg); //메세지를 인자값으로 받아서 출력
result = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
break;
}catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println(er);//이쪽도 인자값으로 받는게 더 좋다.
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("===계산기 프로그램===");
while(true) {
System.out.print("연산자 입력(+,-,*,/) :");
String oper = sc.nextLine();
if(oper.contentEquals("q")) {
System.out.println("계산기 프로그램을 종료합니다.");
System.exit(0);
// }else if(oper.equals("+")||oper.equals("-")||
// oper.equals("*")||oper.equals("/")){ //긍정
}else if(!oper.contentEquals("+") && !oper.contentEquals("-")
&& !oper.contentEquals("*") && !oper.contentEquals("/")) {
System.out.println("연산자를 확인하세요.");
continue;
}
int num1 = inputnumber("첫번째 숫자 :","입력된 값이 숫자가 아닙니다.");
int num2 = inputnumber("두번째 숫자 :","입력된 값이 숫자가 아니라구!");
// while(true) {
// try {
// System.out.print("첫번째 숫자 입력 :");
// num1 = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
// break;
// }catch(Exception e) {
// System.out.println("입력된 값이 숫자가 아닙니다.");
// }
// }
// while(true) {
// try {
// System.out.print("두번째 숫자 입력 :");
// num2 = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
// break;
// }catch(Exception e) {
// System.out.println("입력된 값이 숫자가 아닙니다.");
// }
// }
System.out.println("====== 결 과 ======");
switch(oper) {
case "+" :
System.out.println(num1 +" "+ oper +" "+ num2 +" = "+(num1+num2) );
break;
case "-" :
System.out.println(num1 +" "+ oper +" "+ num2 +" = "+(num1-num2) );
break;
case "*" :
System.out.println(num1 +" "+ oper +" "+ num2 +" = "+(num1*num2) );
break;
case "/" :
System.out.println(num1 +" "+ oper +" "+ num2 +" = "+((double)num1/num2) );
break;
}
}
}
}//call by reference, 참조에 의한 호출
public class Exam_01 {
public static void method(int[] arr) {
arr[2] = 100;
}// 괄호가 닫히면 지역의 변수들 사라짐 (주소값을 가르키는 선도 사라짐)
public static void func() {}
public static void func1(int num) {}
public static void func2(int[] arr) {}
public static int test(int a) { //매개변수 a
// a = 50;
return 50;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// func(); // call by name
// func1(100); // call by value
// func2(new int[] {1,2,3}); // call by reference, 기본자료형이 아닌 주소값으로 호출
int arr[] = new int[] {1,2,3,4,5};
method(arr);// call by reference
// int a = 10;
// a = test(a);
// System.out.println(a);
// Stack 지역변수a[10] 매서드 매개변수a[10->50]->매개변수사라짐
// ______________
// heap
// ______________
}
}Stack arr(main 지역)(주소값을 가짐, 1000번지), arr(매서드 지역)(주소값을 가짐, 1000번지)
______________
heap [ ][ ][ ][ ] (주소 1000번지)
______________
// Stack 지역변수a[10] 매서드의 매개변수a[10->50]->매개변수사라짐
// ______________
// heap
// ______________
- call by reference : 리턴과 인자값에 상관없이 주소값을 넘겨야 main 안의 값을 변환
//로또 시뮬 + method
public class Quiz_01 {
//섞기
public static void shakeIt(int[] lotto) {
for(int i =0; i< 500; i++) {
int x = (int)(Math.random()*45);
int y = (int)(Math.random()*45);
int tmp = lotto[x];
lotto[x] = lotto[y];
lotto[y] = tmp;
}
}
//초기화
public static void initializeArr(int[] lotto) {//지역변수 가져오기
for(int i=0; i<lotto.length; i++) {
lotto[i]=i+1;
}
}
//두 배열 비교하여 매치되는 개수 세기
public static int comfirmation(int[] lotto, int[] trylotto) {
int match=0;
for(int i = 0; i<6; i++) {
for(int j =0; j<6; j++) {
if(lotto[i]==trylotto[j]) {
match += 1;
}
}
}
return match;
}
//메세지와 출력할 번호들
public static String printLotto(String str, int[] trylotto) {
String printLt =
" ("+trylotto[0]+") ("+trylotto[1]+") ("+trylotto[2]+") ("+trylotto[3]+") ("+trylotto[4]+") ("+trylotto[5]+") "+str;
return printLt;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//당첨 배열 생성
int[] lotto = new int[45];
int[] trylotto = new int[45];
initializeArr(lotto); // 배열 1~45까지 초기화
shakeIt(lotto); // 섞기
int count2 =0;
int count3 =0;
int count4 =0;
int count5 =0;
for(int count =0;;count++) { //게속 반복하며 횟수세기
initializeArr(trylotto);
shakeIt(trylotto);
if(comfirmation(lotto, trylotto) == 6) {
System.out.print(count+"번 시도");
System.out.println(printLotto("당첨!", trylotto));
System.out.println(" 1등! 인생역전!!!");
System.out.println("***금주의 당첨 번호***");
System.out.println(printLotto("보너스 번호 : "+lotto[6], lotto));
System.out.println("총 "+ count+"회 시도하여 구입비로"+(count*0.5)+"만원을 사용하였습니다.");
System.out.println("그 동안 2등은 "+count2+"번 당첨되었습니다.");
System.out.println("그 동안 3등은 "+count3+"번 당첨되었습니다.");
System.out.println("그 동안 4등은 "+count4+"번 당첨되었습니다.");
System.out.println("그 동안 5등은 "+count5+"번 당첨되었습니다.");
break;
}else if(comfirmation(lotto, trylotto) == 5) {
//보너스 숫자lotto[6]와 일치하면 2등
for(int i =0; i<6; i++) {
if(trylotto[i]==lotto[6]) {
System.out.print(count+"번 시도");
System.out.print(printLotto("2등", trylotto));
System.out.println(" 보너스번호 : " +trylotto[6]);
count2 += 1;
continue;
}
}
//보너스 숫자와 일치하지 않으면 3등
System.out.print(count+"번 시도");
System.out.println(printLotto("3등", trylotto));
count3 += 1;
continue ;
}else if(comfirmation(lotto, trylotto) == 4) {
//4등
System.out.print(count+"번 시도");
System.out.println(printLotto("4등", trylotto));
count4 += 1;
continue;
}else if(comfirmation(lotto, trylotto) == 3) {
System.out.print(count+"번 시도");
System.out.println(printLotto("5등", trylotto));
count5 += 1;
continue;
}else {
System.out.print(count+"번 시도");
System.out.println(printLotto(" ", trylotto));
continue;
}
}
}
}//가변인자 방식
public class Exam_02 {
public static void func(String... str) { //가변인자 매개변수
for(int i = 0 ; i< str.length; i++) {
System.out.println(str[i]);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
func("Hello"); //인자값이 몇개인지 모르는 상황
func("Hello","World");
}
}//method 같은 이름으로 2개 만들 수 없다.
//C언어에서는 절대 중복 안됨
//C++ 이후 부터는
//매서드의 이름이 같아도, 매개변수의 종류 또는 개수가 다르면
//다른 매서드로 인식한다.
//자바의 Method Overloading 과적하다.
//리턴값은 오버로딩의 기준이 되지 못한다.
public class Exam_03 {
public static void func(){
System.out.println("A");
}
public static void func(int num){
System.out.println("B");
}
public static void func(double b){
System.out.println("C");
}
public static void func(int num1, int num2){
System.out.println("D");
}
// public static void fun(){}
// public static int fun(){}
public static void main(String[] args) {
func();
func(100);
func(100.0);
func(50,20);
System.out.println();//double int String 매개변수마다 모두 만들어져 있음
}
}
OOP (객체지향 프로그래밍)
- 객체지향 프로그램 Objrct Oriented Programming
- 1960년대 과학적 또는 군사학적 모의 실험 (Simulation) 분야에서 활용하기 위해 만들어진 개발이론
- 현실에 대한 모델링을 기본으로 하며, 속성과 기능을 가지는 객체간의 관계에 따른 프로그램 흐름이 특징
- 당시 절차지향 기반의 Fortran 또한 Cobol 등의 언어가 입지를 다지던 시기로 세간의 주목을 끌지 못 함
- 1980년대 후반 Software Crisis를 극복하기 위한 개발 방법론으로 대두되며 C++이나 Small talk 등의 언어가 등장 했으나 흥행에 실패
- 1995년 자바언어가 체계화된 객체지향언어로 등장하며 현대 개발 패러다임의 주축으로 등극
- 절차지향은 강력하고 최적화된 컴팩트한 언어이지만 생산성이 떨어짐
- 객체지향 코드
- 개발 대상의 선택
- 개발 대상의 분석
- 개발 대상에 대한 속성과 기능을 명세
- ex. 모니터
- 속성 : 색깔 / 가격 / 브랜드 ...
- 기능 : 전원 켜기, 끄기 / 밝기 조정 / 해상도 조정 ...
- 개발 대상 설계도 작성
- class Monitor{ }
- 우리가 만든 class들은 특수 클래스(main method 포함), 대부분은 설계도 목적의 class
- Java에서는 class가 기본단위
- 프로그램이 시작되려면 main method 실행용 class가 1개는 있어야함
class Monitor{ // class의 첫글자는 대문자여야 한다.(자바 글로벌 컨벤션)
//자바에서는 클래스와 상수만 첫글자가 대문자. (상수는 전체 대문자)
int price; //속성은 변수
String color;
void powerOn(){}
void powerOff(){}
void brightnessUp(){}
void brightnessDown(){}
}
//설계도로 만든 클래스는 참조 자료형
//heap 메모리에 만들어지기 때문에 new를 써야 한다import java.util.Scanner;
public class Exam_04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Monitor mon;
//Stack mon(주소저장을 위한 공간)
//Data
//Heap
//Text
//_________실제로 만들어지지는 않음
Monitor mon = new Monitor(); //heap에다가 만든다 //메모리의 주소값
//Stack mon(주소저장을 위한 공간)
//Data
//Heap 실체 데이터 생성 (instance,객체,new연산자를 통해 힙메모리에 실체화된 데이터)
//Text
//_________모니터가 만들어지면 그 주소값이 리턴
// Scanner sc = new Scanner();
// String str = new String(); // 첫글자 대문자, class, 참조자료형
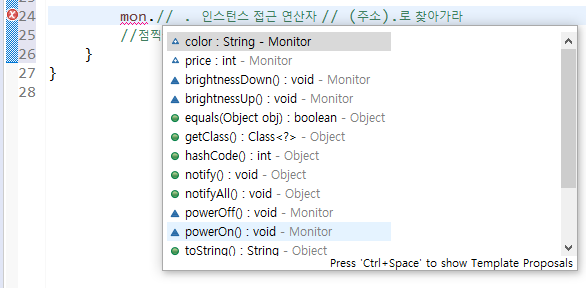
mon.powerOn();// . 인스턴스 접근 연산자 // (주소).로 찾아가라
//점찍을 때 나오는 박스 : 왜 찾아오셨어요?
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); //JRE시스템라이브러리에 있는 클래스
sc.nextLine(); //대상의 기능들 method
//method별로 Stack에 독자적 공간을 만들어서 한줄씩 실행, 그사이에 변수가 나타나면 Text에 저장
//method 내에 있는게 지역변수
//지역변수 말고 class 안에 있는 변수는 멤버변수, 인스턴스의 생존여부에 따라 존재
//powerOn메소드 실행될때 Stack에 생성후 실행끝나면 삭제, 지역변수, method의 실행여부에따라 존재
//래퍼런스가 끊겼을때 인스턴스가 사라진다.
}
}
- method별로 Stack에 공간을 만들어서 한줄씩 실행, 그사이에 변수가 나타나면 Text에
- method 내에 있는게 지역변수
- 지역변수 말고 class에 있는 변수는 멤버변수
//가변적이기 때문에 heap메모리에 저장되는 참조자료형, new를 써야함
//
public class Monitor {
int price; //속성은 변수
String color;
void powerOn(){//매서드틑 텍스트메모리로 (코드영역,매서드영역)
int a; // 로컬필드, 로컬버라이어블
}
void powerOff(){} //메서드의 첫글자는 대문자일수 없음,카멜케이스
void brightnessUp(){}
void brightnessDown(){}
// Constructor : 생성자
// Nested Class : 중첩클래스
}정보은닉
- -> 접근제한자
- public > protected > package > private
- public, private이 가장 빈번하게 쓰임
- public : 프로젝트 내의 모든 곳에서 접근 가능
- private : 접근 차단, 중괄호를 벗어난 곳에서는 접근 불가

- 정보은닉 : private으로 정보를 숨긴다.
- 장점1: 개발자의 의도대로 사용자가 오동작를 일으키지 않도록 제어 가능, 개발자의 통제, 안전성
- 모든 상황에 정답은 아니지만 관습적으로 멤버필드는 private을 붙인다.
- 외부에서 건드려야 한다면 , method를 통해서 조작
- 장점2: 외부에 공개할 필요가 없는(공개해서는 안되는) 내용을 숨기기 위해서, 사용자의 편의성
public class Monitor {
private int price; //접근 차단, 중괄호를 벗어난 곳에서는 접근 불가,
private String color; //프라이빗 필드를 조작할 메서드 제공
public void setPrice(int pr) { //리턴값 없음 void
price = pr;
//매개변수가 값을 받고 method끝나면 사라짐, 사라지기전에 price에 넣어주자
}
public void setColor(String co) {
color = co;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
}
public class Exam_04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Monitor mon = new Monitor();
mon.setPrice(1000);
// System.out.println(mon.price); //정보은닉, 못꺼낸다.
System.out.println(mon.getPrice());
//꺼내오는method, 넣을 인자값은 필요없지만 가져올 리턴값은 필요
mon.setColor("Red");
System.out.println(mon.getColor());
}
}

public class Monitor {
private int price; //heap
private String color;
// private final Monitor this;
//작성을 하지 않았지만 작성한 것으로 취급하는 암묵적 문법 중 하나
//자기참조변수 문법은 작성하면 안됨 (cf. import java.lang.*)
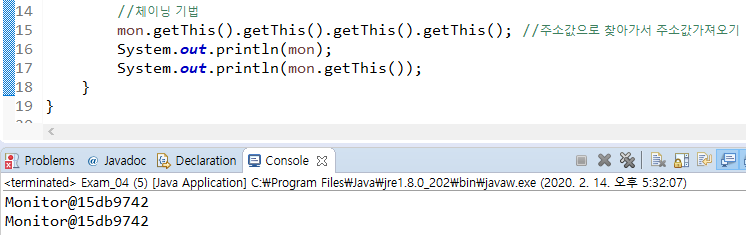
public Monitor getThis() {
return this;
}
public void setPrice(int price) { //자바 개발자들은 멤버필드와 매개변수 이름을 똑같이 짓는다
//멤버필드와 매개변수를 똑같이 지을 경우, 매개변수=매개변수 (Stack메모리의 매개변수가 가까우므로)
//this가 앞에 붙으면 멤버필드가 된다.
//매개변수는 멤버가 아니라 method의 소유
this.price = price;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
}- 자바 개발자들은 멤버필드와 매개변수 이름을 똑같이 짓는다
- 멤버필드와 매개변수를 똑같이 지을 경우
- 매개변수=매개변수 (Stack메모리의 매개변수가 가까우므로)
- this가 앞에 붙으면 멤버필드가 된다.
- 매개변수는 멤버가 아니라 method의 소유
- this(자기참조변수)
- 클래스내부에서는 내 필드와 기능을 볼수 없음 (외부에서는 주소값. 찍으면 나옴)

'디지털 컨버전스 > JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] FTP (1) | 2020.02.18 |
|---|---|
| [Java] member field , Constructor, 정적 변수, 라이브러리, FTP (0) | 2020.02.17 |
| [Java] Method (0) | 2020.02.13 |
| [Java] 배열 (0) | 2020.02.12 |
| [Java] 가위바위보, UP&DOWN, 경마, 베스킨라빈스 (0) | 2020.02.11 |